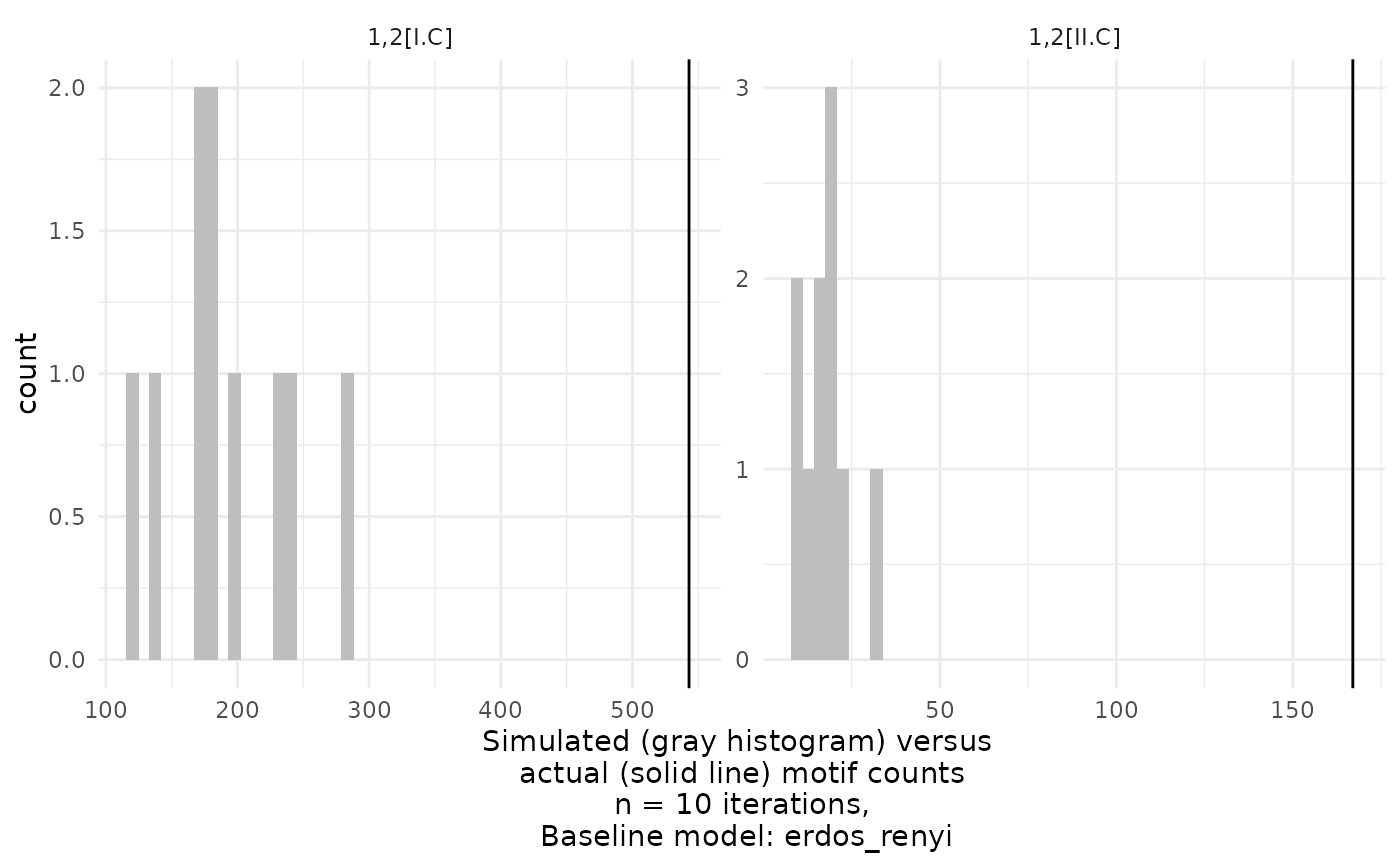
Compare motif occurence in empirical network to occurence in a baseline model
Source:R/count_motifs.R
compare_to_baseline.RdThis function plots a comparison of the motif counts in a given network with the motif counts in a baseline model.
compare_to_baseline( net, motifs, n = 10, lvl_attr = "sesType", assume_sparse = TRUE, model = "erdos_renyi", level = -1, ergm_model = NULL, directed = NULL )
Arguments
| net | network object |
|---|---|
| motifs | list of motif identifier strings |
| n | number of random graphs used in baseline model |
| lvl_attr | character vector specifying the attribute name where level
information is stored in |
| assume_sparse | whether the random graphs shall be assumed to be sparse. used to find ideal counting function |
| model | baseline model to be used. Options are 'erdos_renyi', 'actors_choice',
'ergm', 'partial_ergm' and fixed_densities'.
See |
| level | lvl_attr of the variable level for the Actor's Choice model |
| ergm_model | ergm model as for example fitted by calling
|
| directed | whether the graph shall be treated as a directed graph. Per
default ( |
Value
data frame with one row for each motif identifier string and one row for every computed random graph
Details
Note that when using the Actor's Choice model this function does not choose
the variable level automatically. Use the level parameter to provide a
valid level.
When using ERGM the parameter net is not used. Networks to create the
baseline from are sampled in R using the ergm_model parameter.
Examples
# }